The oldest known manuscripts of the New Testament were written in Greek, but by comparing Matt. 1:21 in Hebrew, Aramaic and Greek with the knowledge of the naming formula so common in the Hebrew Bible, we see that this verse only makes sense in Hebrew. Since the naming formula depends on a wordplay that does not work in Greek or Aramaic, Matt. 1:21, or the oral tradition behind it, had to be in Hebrew.
The Major Importance of the “Minor” Agreements

In this article, Dr. Robert Lindsey discusses the importance of the so-called “minor agreements” of Luke and Matthew against Mark for properly understanding the interrelationship of the Synoptic Gospels. David N. Bivin and Joshua N. Tilton collaborated with Lauren Asperschlager to bring this article, which previously existed only as an unfinished draft, to Jerusalem Perspective subscribers.
Notley Lecture: “Between the Chairs: New Testament Evidence for the Hebrew Jesus Spoke”

Dr. R. Steven Notley is a contributor to Jerusalem Perspective and member of the Jerusalem School of Synoptic Research. He is Professor of New Testament and Christian Origins at Nyack College in New York. In this lecture Dr. Notley discusses examples of how the Hebrew language influenced the Greek text of the canonical Gospels.
The Hebrew Life of Jesus

Despite the popularity of the modern suggestion that the Synoptic Gospels are the end result of several decades of oral transmission, the internal evidence indicates that this is not the case. Dozens of pericopae in Matthew and Luke translate to Hebrew so easily and so idiomatically that we must conclude that the Synoptic Gospels are the result of literary transmission.
1987 Interview with Dr. Robert Lindsey

In 1987 Robert Lindsey conducted an interview in which he discussed many aspects of his life and ministry. In the following clips Dr. Lindsey discusses the usefulness of knowing Hebrew for a proper understanding of Jesus’ message.
“Verily” or “Amen”—What Did Jesus Say?

In translating the Greek texts of the Gospels into Hebrew, Dr. Lindsey found that many passages could be rendered literally with almost no change of word order. The result was a Hebrew version that often sheds fascinating light on the meaning of Jesus’ words, so much so that Lindsey came to believe the Greek sources Matthew, Mark and Luke used were rendered very literally from Hebrew originals. This Hebraic perspective sometimes explains Gospel passages that have long been considered difficult or ambiguous. In the following article, Lindsey presents one example of what has been considered a uniquely idiosyncratic expression of Jesus, but which a Hebraic perspective reveals to be a familiar phrase from the Scriptures.
Hebraisms in the New Testament

The text of the New Testament contains many Semitic elements, some of which are Hebraisms. The Synoptic Gospels show evidence for the existence of wordplays and idioms that are typical of Hebrew.
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Five (Parallelism)

Parallelism is a central feature of Hebrew poetry. It permeates the words of biblical poet and prophet. The frequency with which parallelism occurs in the utterances of Jesus is surprising, and leads inevitably to the conclusion that the Greek source (or, sources) used by the authors of Matthew, Mark and Luke derive(s) from a Greek translation (or, translations) of Hebrew documents.
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Two (Luke 9:51-56)

Relatively few of the suggested Semitisms underlying the Greek New Testament constitute clear-cut proof for a Hebrew undertext, but a high density of Hebraisms in a given passage increases the probability that it is “translation Greek.”
Why Learn to Speak a Dead Language?
Why would anyone in his or her right mind want to speak a “dead” language, a language that no one speaks? The answer: Because only by speaking a language does one internalize it, and it was high time, Randall and I felt, having tasted fluency in Hebrew, that we should gain an active knowledge of Koine Greek.
What’s Happening to the Holy Tongue?
English speakers who live in Israel are reminded regularly of the inroads English is making in Hebrew.
Hebrew or Aramaic? Some Evidence from Inscriptions
The fundamental assumptions of the past of Jesus’ mother tongue are again and again repeated today while their frame of reference has changed dramatically.
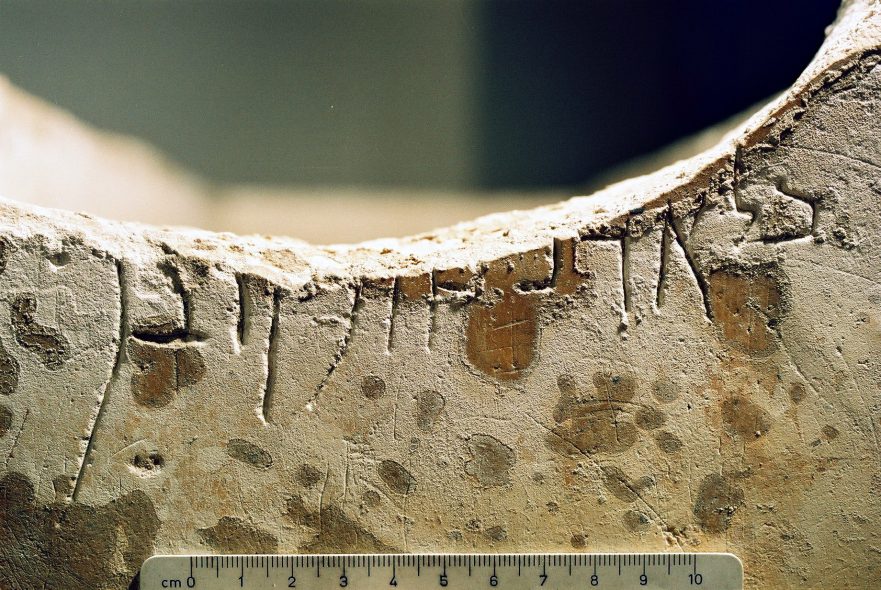
Hananiah Notos: The Never-ending Importance of the Dead Sea Scrolls
One of the recently published Dead Sea Scroll documents is known as the “Register of Rebukes.” Only parts of eleven lines of a column of this document have survived. However, even these few words and parts of words are enough to see that the document, or a portion of it, was a list of the sect’s members who were rebuked because they had violated community laws.
Call No Man “Father”

The word abba (אַבָּא), which literally means “the father” in Aramaic, but also can mean “our father” or “my father,” was brought into Hebrew and used in the endearing sense of “daddy.”
Another Look at the “Cleansing of the Temple” Story
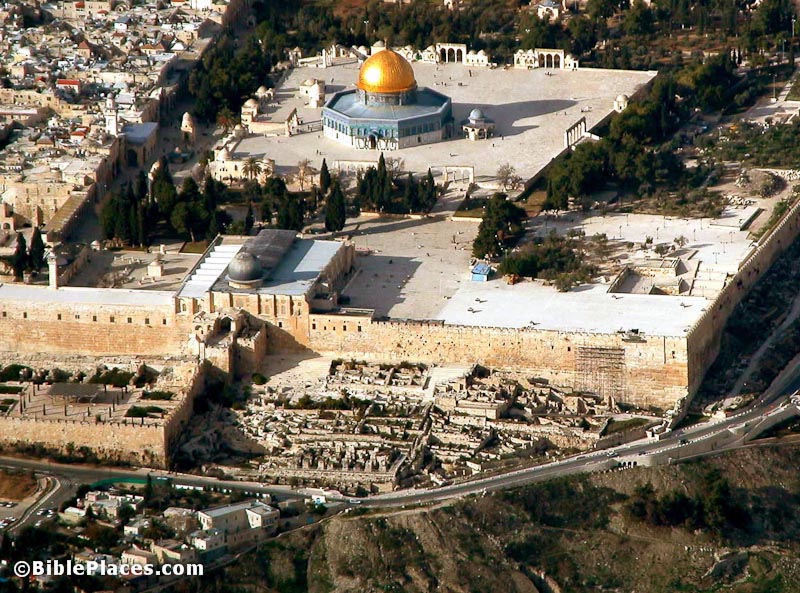

Based on archaeological excavations near the southern wall of the temple, the research of Shmuel Safrai, and a nuance of the Hebrew verb that is one of the equivalents for Greek ekballein (drive out, banish; throw out; throw away, reject; cast out of a place, expel; remove, get rid of; put out), it may be necessary to reinterpret the gospel accounts of Jesus’ “cleansing” of the temple, even suggesting a different location for Jesus’ action.
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part One (Luke 10:23-24)

Hebrew idioms leap out from every page of Jesus’ life story.
Let the One Who Has Ears to Hear, “Hear!”

Gospel parables are probably the most widely identifiable teaching form of Jesus. However, readers seldom recognize Jesus’ sophisticated skill as a first-century Jewish parabolist. Indeed, many Christians are unaware that his use of story parables is one of the strongest links between Jesus and contemporary Jewish piety. His parables also demonstrate that Jesus taught in Hebrew.
More on the Absence of an Aramaic Bible at Qumran: A Response to Jack Poirier’s “The Qumran Targum of Job as a Window into Second Temple Judaism: A Response to Randall Buth”

I appreciate this opportunity to return to some issues concerning the Targum of Job that I raised in Where Is the Aramaic Bible at Qumran? Scripture Use in the Land of Israel and to evaluate Jack Poirier’s response entitled, The Qumran Targum of Job as a Window into Second Temple Judaism: A Response to Randall Buth.

