My wife, Lenore, and I have dealt with a great many people who, because of various circumstances in their life, are unable to feel loved—by God or anyone else. In fact, they often describe how they feel as “numb” or “empty.” They often view themselves as unattractive, unlovable, and worthless. This is in spite of the fact that many of these people are considered successful in their chosen field.
Blessedness of the Twelve

Without a knowledge of the saying’s context, Jesus’ saying about eyes and ears and prophets and righteous men, seems quite prosaic. However, when it is understood that this saying deals with the Kingdom of Heaven, it becomes one of Jesus’ most exciting and dramatic statements.
Lord’s Prayer

David Bivin and Joshua Tilton envision how the Lord’s Prayer might have been formulated in its original language and explore the ancient Jewish context to which the Lord’s Prayer belongs.
Preparations for Eating the Passover Lamb

Careful analysis shows that a Hebraic source ultimately stands behind the Synoptic Gospels and that this source is best preserved in Luke. Luke’s version of the Preparations for Eating Passover Lamb preserves details—such as Jesus taking the initiative to send the two disciples, commanding the disciples to prepare the lamb, and using Hebraic idiom—that fit the cultural context of first-century Judaism.
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Six (Parallelism)

In this article, we will discuss the second type of parallelism: Antithetical Parallelism.
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Four (Parallelism)

Doubling, or repeating, is a characteristic feature of Hebrew. Hebrew loves to say things twice (or more!) by adding equivalents. Words, phrases, sentences, and even stories, are doubled (or tripled).
Cataloging the Gospels’ Hebraisms: Part Three (Impersonal “They”)

Awareness of even the simplest Hebrew grammatical structure can bring to life a vague, or difficult-to-understand, saying of Jesus. Since potential Hebrew idioms are so dense in the Greek texts of Matthew, Mark and Luke, one has to ask, Could these apparent Hebrew idioms be evidence that the synoptic Gospels are descendants of an ancient translation of a Hebrew “Life of Jesus,” the gospel that the church father Papias spoke of when he wrote: “Matthew…arranged the sayings [of Jesus] in the Hebrew language”?
The “Hypocrisy” of the Pharisees

Without reading the Scriptures carefully, and without a familiarity with Second Temple-period extra-biblical sources, a simple reader of the New Testament might assume that a majority of the Pharisees were hypocrites and that the Pharisees as a movement were indeed a “brood of vipers.” As a result of this common Christian assumption, the word “Pharisee” has become a synonym for “hypocrite” in the English language.
Evidence of an Editor’s Hand in Two Instances of Mark’s Account of Jesus’ Last Week?
It has been noted that in instances where Mark’s editorial hand restructured his story, Luke has preserved a more primitive form of the account, a form that is independent of Mark’s influence. Gospel scholars need to properly evaluate Mark’s editorial style and acknowledge that frequently a theological agenda influenced his rewriting.
Jesus and the Enigmatic “Green Tree”

Jesus made bold messianic claims when he spoke. To thoroughly understand these claims, however, we must get into a time machine and travel back in time to a completely different culture, the Jewish culture of first-century Israel. We must acculturate ourselves to the way teachers and disciples in the time of Jesus communicated through allusions to Scripture.
Keys of the Kingdom: Allusion to Divinity?
The more we know and understand the historical, cultural and linguistic background of the Bible, the more we are able to discern elements in the biblical text that heretofore have gone unnoticed. These can be elements that can greatly increase our understanding of the biblical text, reinforce our traditional conceptions, or at times radically transform our understanding by revealing totally unexpected information that affects how the texts would have been originally understood.
The Value of Rabbinic Literature as an Historical Source

The thesis of this article is that rabbinic sources, when used in a careful manner, can provide reliable historical material pertaining to the Second Temple period. If this thesis is accepted, the consequences for the study of the New Testament Gospels are obvious.
Mark 7:19: Did Jesus Make “Unclean” Food “Clean”?

One should not be too quick to throw out large portions of the Torah because of a four-word parenthetical comment by Mark at the end of a long halachic discussion.
Links with Tabernacles and Hanukkah in the Gospel Accounts of Palm Sunday

The Gospel writers wished their readers to be reminded of Hanukkah when they read the account of Palm Sunday.
Treasures in Heaven

What is the relationship between the preaching of Jonah and putting a lamp on a lampstand? The prophet Jonah in classical Jewish thought calls to mind repentance. In Rabbinic literature we read that many prophets were sent to Jerusalem and the people did not listen, but to Nineveh one prophet was sent, and the people repented.
Sunshine For Everybody

Song of Songs Zuta is a rabbinic commentary on the Song of Songs. It may be characterized as exegetical and haggadic. In contrast to the better known Song of Songs Rabbah, Song of Songs Zuta is shorter in length. The words rabbah (great) and zuta (small) imply this contrast.
Threading a Needle
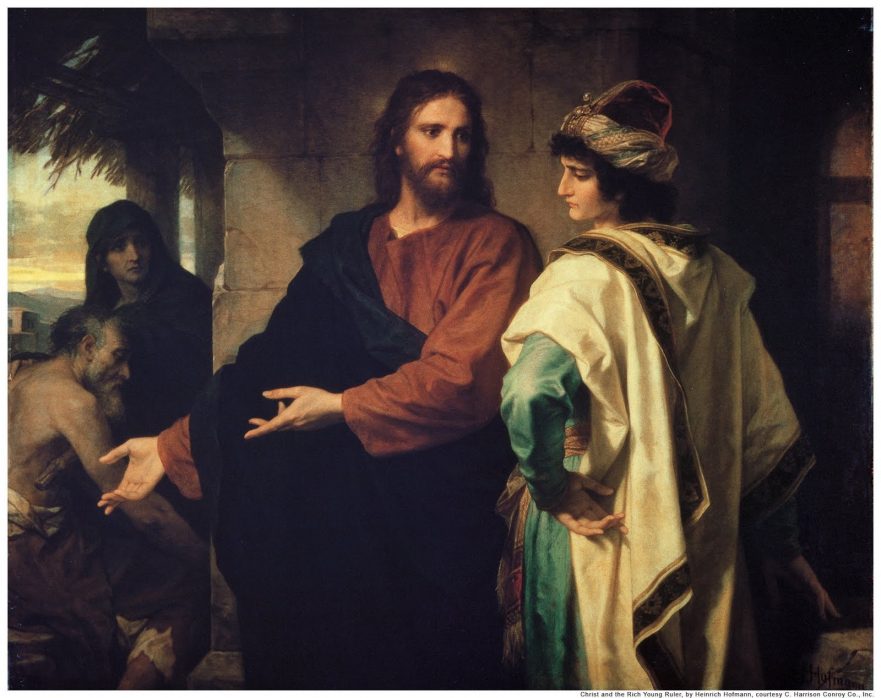

Over the past few years, I have reflected much on the phrases “to enter the Kingdom of Heaven” and “to inherit eternal life.” One important conclusion that I have reached from reading early rabbinic literature and Matthew, Mark, and Luke is that these are two independent concepts sharing a fuzzy area of overlap.