Listen to a recent recording of the Lord’s Prayer sung in Greek in the style of a Gregorian chant.
Why Do You Call Me ‘Lord’?: On the Origins of Jesus’ Dominical Title

The confession “Jesus is Lord” is the simplest and earliest Christian creed. But how did referring to Jesus as “Lord” begin?
The Names of Jerusalem in the Synoptic Gospels and Acts

What can the Greek and Hebrew forms of Jerusalem’s name tell us either about the sources of the Synoptic Gospels and Acts or the audiences to whom these works were addressed?
Cumulative Life of Yeshua Greek Reconstructions

The reconstructed Greek text of the Anthology (thus far completed) with accompanying English translation.
LOY Excursus: The Genitive Absolute in the Synoptic Gospels

What can the distribution of genitive absolute constructions in the Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke tell us about the origins of the Synoptic Gospels?
Evidence for Hebrew Roots of Matthew 1:21

The oldest known manuscripts of the New Testament were written in Greek, but by comparing Matt. 1:21 in Hebrew, Aramaic and Greek with the knowledge of the naming formula so common in the Hebrew Bible, we see that this verse only makes sense in Hebrew. Since the naming formula depends on a wordplay that does not work in Greek or Aramaic, Matt. 1:21, or the oral tradition behind it, had to be in Hebrew.
Notley Lecture: “Between the Chairs: New Testament Evidence for the Hebrew Jesus Spoke”

Dr. R. Steven Notley is a contributor to Jerusalem Perspective and member of the Jerusalem School of Synoptic Research. He is Professor of New Testament and Christian Origins at Nyack College in New York. In this lecture Dr. Notley discusses examples of how the Hebrew language influenced the Greek text of the canonical Gospels.
LOY Excursus: Greek Transliterations of Hebrew, Aramaic and Hebrew/Aramaic Words in the Synoptic Gospels

One of the clues that the Synoptic Gospels descended from a Hebrew Life of Yeshua is the number of foreign words that were transliterated into Greek from either Hebrew or Aramaic (it is often impossible to distinguish Hebrew from Aramaic in Greek transliteration).
“Treasure in Heaven”: Examining an Ancient Idiom for Charity

The growing value placed on charity in the first century C.E. cannot be overstated. As a new sensitivity developed within Judaism that challenged the compensatory “blessings and curses” paradigm of the Hebrew Bible (cf. Deut. 28) as a basis to serve God, so there was a shifting emphasis towards altruistic love embodied in the Levitical commandment, “…and you shall love your neighbor as yourself (וְאָהַבְתָּ לְרֵעֲךָ כָּמוֹךָ אֲנִי יי; Lev. 19:18).”
“Verily” or “Amen”—What Did Jesus Say?

In translating the Greek texts of the Gospels into Hebrew, Dr. Lindsey found that many passages could be rendered literally with almost no change of word order. The result was a Hebrew version that often sheds fascinating light on the meaning of Jesus’ words, so much so that Lindsey came to believe the Greek sources Matthew, Mark and Luke used were rendered very literally from Hebrew originals. This Hebraic perspective sometimes explains Gospel passages that have long been considered difficult or ambiguous. In the following article, Lindsey presents one example of what has been considered a uniquely idiosyncratic expression of Jesus, but which a Hebraic perspective reveals to be a familiar phrase from the Scriptures.
Hebraisms in the New Testament

The text of the New Testament contains many Semitic elements, some of which are Hebraisms. The Synoptic Gospels show evidence for the existence of wordplays and idioms that are typical of Hebrew.
Evidence of an Editor’s Hand in Two Instances of Mark’s Account of Jesus’ Last Week?
It has been noted that in instances where Mark’s editorial hand restructured his story, Luke has preserved a more primitive form of the account, a form that is independent of Mark’s influence. Gospel scholars need to properly evaluate Mark’s editorial style and acknowledge that frequently a theological agenda influenced his rewriting.
Jesus and the Enigmatic “Green Tree”

Jesus made bold messianic claims when he spoke. To thoroughly understand these claims, however, we must get into a time machine and travel back in time to a completely different culture, the Jewish culture of first-century Israel. We must acculturate ourselves to the way teachers and disciples in the time of Jesus communicated through allusions to Scripture.
Why Learn to Speak a Dead Language?
Why would anyone in his or her right mind want to speak a “dead” language, a language that no one speaks? The answer: Because only by speaking a language does one internalize it, and it was high time, Randall and I felt, having tasted fluency in Hebrew, that we should gain an active knowledge of Koine Greek.
What’s Happening to the Holy Tongue?
English speakers who live in Israel are reminded regularly of the inroads English is making in Hebrew.
My Knowledge of Greek: An Embarrassment for Too Long!
Until recently, I, a New Testament scholar, was often embarrassed by my level of Greek fluency, even after 35 years of studying this ancient biblical language using the traditional grammatical approach. A lack of true fluency in Greek, active knowledge of the language as opposed to passive, is a scourge. Finding myself in this situation, my disappointment was real, but it was kept hidden from my students.
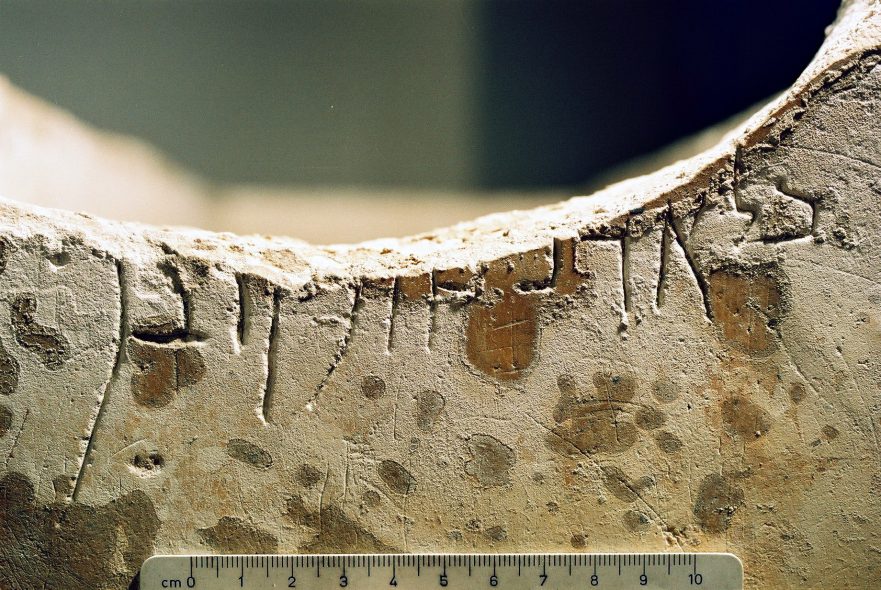
Hebrew or Aramaic? Some Evidence from Inscriptions
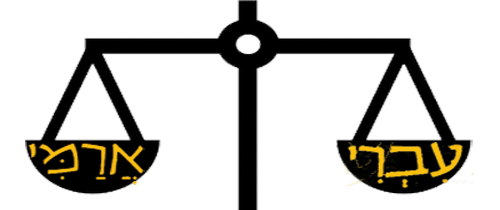
The fundamental assumptions of the past of Jesus’ mother tongue are again and again repeated today while their frame of reference has changed dramatically.
Jehovah and PIPI

According to Jerome, those who were unfamiliar with Jewish customs tried to pronounce the Hebrew letters as if they were Greek letters. The result was quite a howler: they pronounced YHVH as PIPI!

