Does concern for ritual purity explain why the hemorrhaging woman touched Jesus’ tzitzit?
Man With Edema

According to Jesus God sets aside his divine prerogatives in order to alleviate human suffering.
Coordinating Ritual and Moral Purity in the New Testament

Taking another look at how John the Baptist, Jesus, and the Apostle Paul related to issues of ritual and moral purity.
What’s Wrong with Contagious Purity? Debunking the Myth that Jesus Never Became Ritually Impure

The view that Jesus could not be affected by impurity and that Jesus was able to spread his purity to others is based on faulty assumptions and invalid inferences.
Halakha in the Gospels

The Gospels describe Jesus and his followers as keeping halakha to a relatively high extent; they were a group to whom the law was important.
He Could No Longer Openly Enter a Town: A Synoptic Study in Light of an Early Luke

According to Mark, after one of Jesus’ very first miracles, Jesus would no longer openly approach a town in public, but instead avoided the crowds who continually sought him out.
Two Neglected Aspects of the Centurion’s Slave Pericope

Ritual impurity and the tensions resulting from Roman imperialism are two aspects of the Centurion’s Slave pericope that often go overlooked.
Possessed Man in Girgashite Territory

Holiness and purity play a hidden role in the story commonly known as the Gerasene Demoniac.
Yeshua’s Immersion
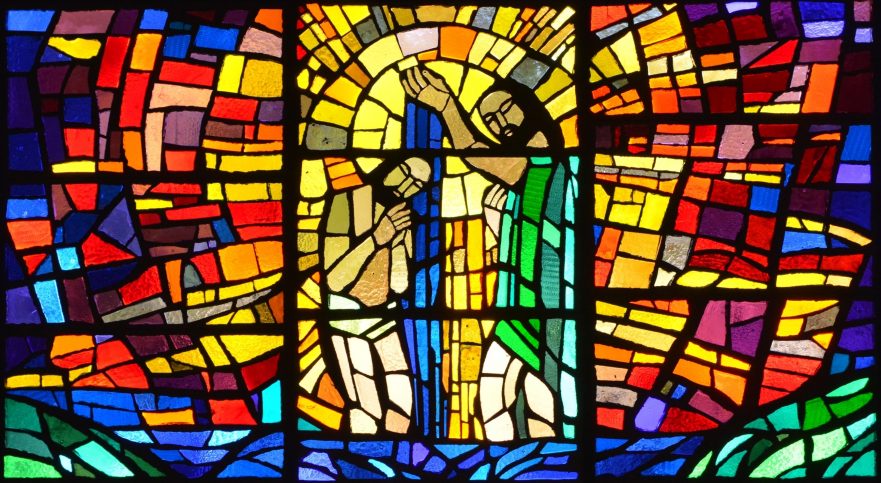

The words of the heavenly voice that spoke at Jesus’ immersion foreshadowed the trajectory of Jesus’ career.
Yohanan the Immerser’s Eschatological Discourse

John the Baptist anticipated the coming of an Elijah-like priestly messiah who would purify the Temple on an eschatological Day of Atonement.
A Voice Crying
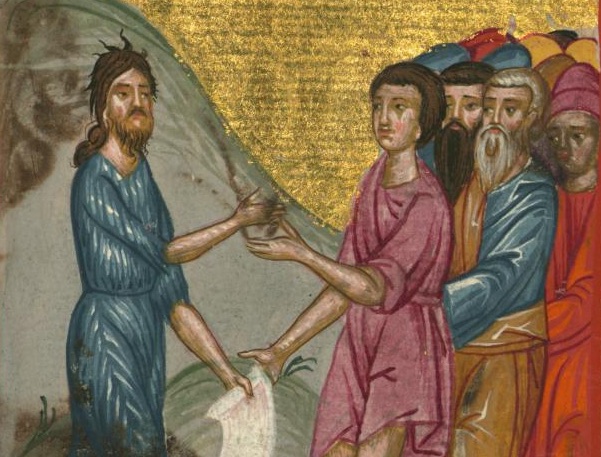

An examination of the Jewish setting of John the Baptist’s proclamation of an immersion of repentance for the release of Israel’s sin indebtedness.
The Mikveh and Ritual Immersion in Jesus’ Day

The complete 2006 lecture is now accessible to JP users. View now!
The Programmatic Opening of Jesus’ Biography as a Reflection of Contemporaneous Jewish Messianic Ideas

In this study Professor Ruzer suggests that there was a broader first-century Jewish context behind the narrative strategies employed in Mark’s prologue to Jesus’ messianic biography. On the other hand, he also demonstrates that Mark 1:9-11 can be used to recover an early phase of a pattern of messianic belief, seemingly shared by wider Judaism, that continued into the rabbinic period. In other words, New Testament evidence can be an important witness to broader trajectories in early Jewish messianic beliefs.
Sending the Twelve: Conduct in Town
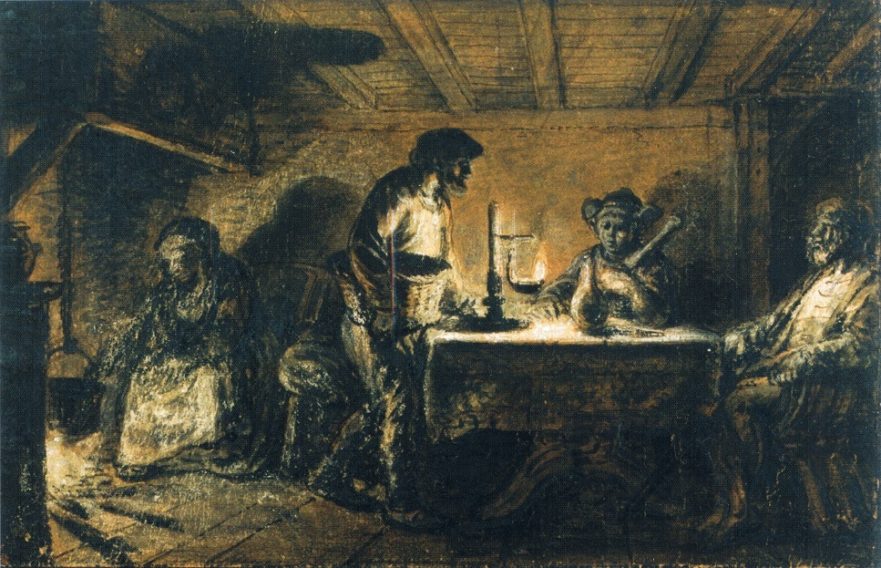

David N. Bivin and Joshua N. Tilton suggest a Hebrew reconstruction of Jesus’ instructions about how the twelve apostles were to behave when they entered a town. In this pericope we learn about the giving and receiving of hospitality among Jesus’ earliest followers. We also learn what may be wrong about the popular view that shaking the dust from the apostles’ feet was a symbolic action meant to signal to Jews who rejected Jesus that they were henceforth to be considered as Gentiles.
“Shake the Dust from Your Feet”: What Did the Apostles’ Action Signify?
The standard interpretation of the apostles’ dust-shaking action proposes that Jesus turned the concept of the impurity of Gentile lands against the Jewish inhabitants of cities within the (ritually pure) land of Israel. This interpretation concludes that shaking the dust from their feet dramatically symbolized that Jesus’ apostles would henceforth regard the Jewish inhabitants of a city that had rejected their message as though they were cut off from Israel. It is time for this mistaken interpretation to finally be put to rest.
The Good Samaritan

The parable of the Good Samaritan came as a response to the lawyer’s question, “And who is my neighbor?” The lawyer wanted Jesus to draw a circle defining who is inside, and therefore the neighbor I must love, and who is outside. Jesus, by using Leviticus 19:34, ingeniously turned the lawyer’s question on its head.
This article is a sample chapter of Marc Turnage’s, Windows into the Bible: Cultural and Historical Insights into the Bible for Modern Readers (Springfield, Mo.: Logion, 2016), which will be released at the end of March 2016.
The Recently Discovered Pool of Siloam
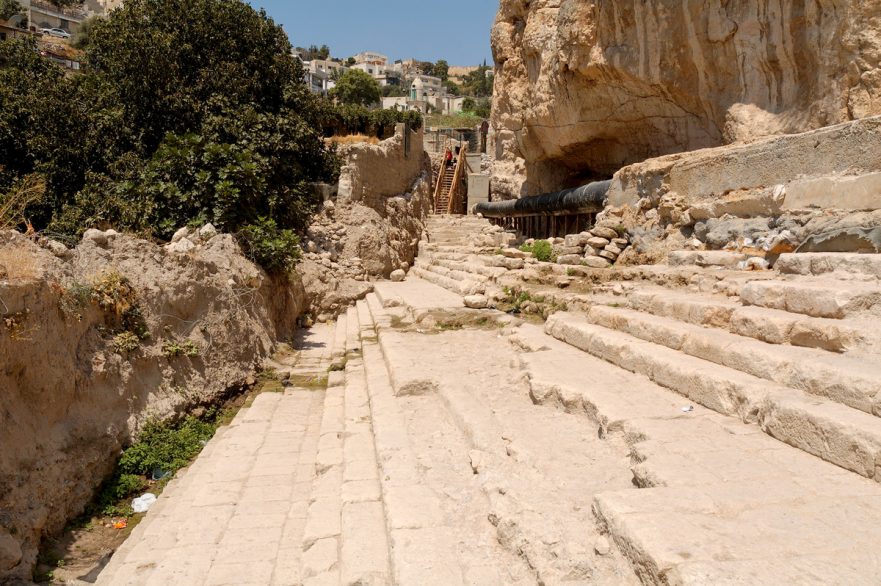

In this free sample lecture from the 2006 Jerusalem Perspective Conference, archaeologist and JP contributor Ronny Reich discusses the excavation of the first-century remains of the pool of Siloam discovered in Jerusalem. The complete collection of presentations delivered at the 2006 Jerusalem Perspective Conference is available through the En-Gedi Resource Center.
- Page 1 of 2
- 1
- 2

